Welcome to RAINER - your personal assistant for troubleshooting in R!
RAINER helps you resolve errors, understand unexpected outputs, and improve your code using a large language model (LLM). It examines the current state of your workspace and code to provide individual explanations and suggestions.
Overview
-
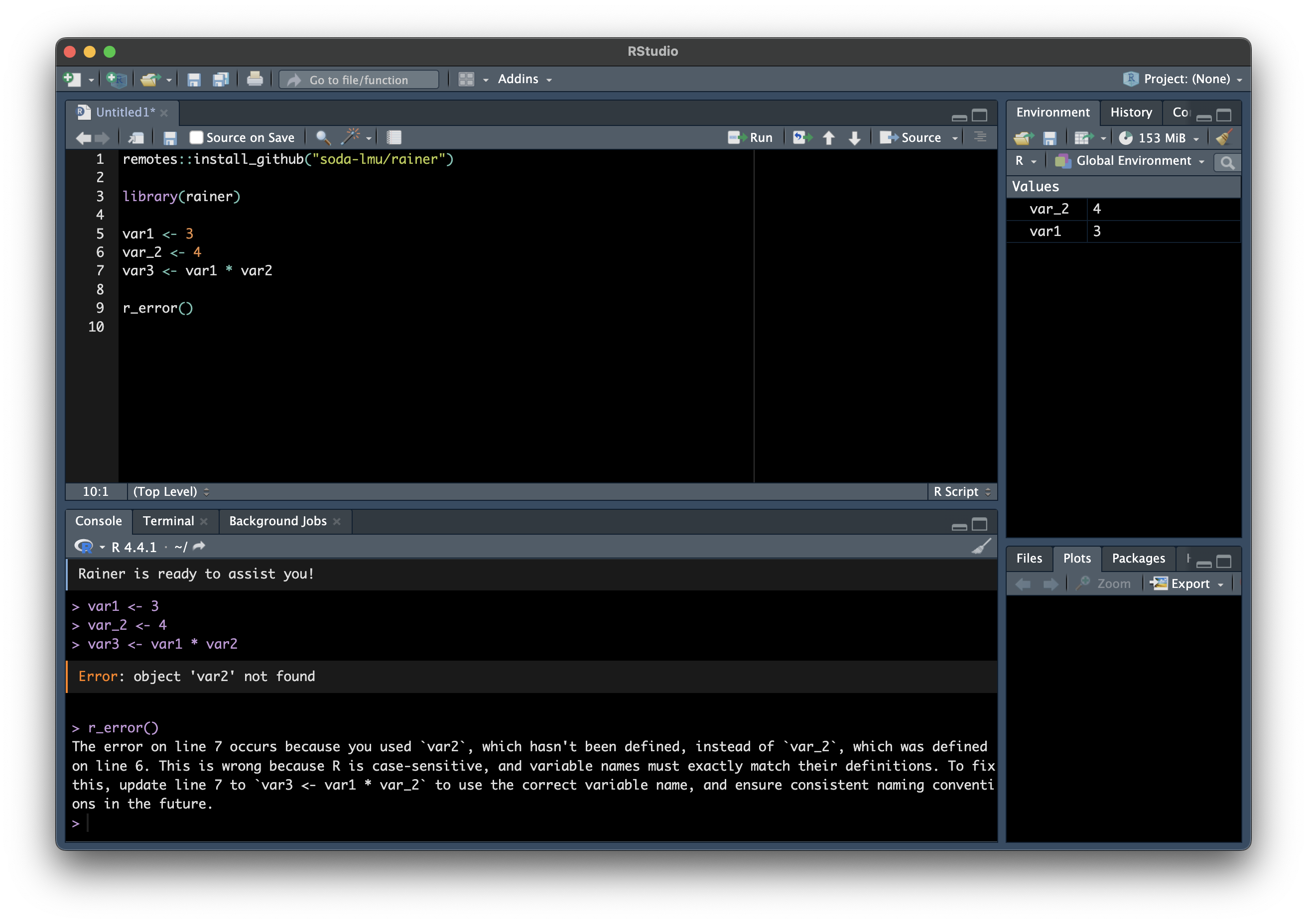
r_error(): Explains error messages, their causes, and how to fix them -
r_activate(): Automatically triggersr_error()whenever an error occurs -
r_explain(): Helps diagnose why an output (e.g., a table) differs from your expectations -
r_improve(): Provides recommendations to enhance your code’s efficiency and clarity.
Installation
RAINER is currently not available on CRAN (yet), but can be installed directly from GitHub. To install the package, use the command below.
# If you have not installed it yet, install the pak package first
install.packages("pak")
# Install RAINER
pak::pak("soda-lmu/rainer")Getting Started
When you load RAINER for the first time, you will be guided through the setup process. RAINER will prompt you to provide information, which will be securely stored on your computer, so you only have to answer them once. More detailed information on the questions can be found below. Please also have a look at the video we recorded, walking you through the first setup incl. retrieving a GitHub token.
- Accepting the data protection regulations
- Your GitHub token (see below on how you can get one)
- Your preferred language (German 🇩🇪 or English 🇬🇧)
- Whether or not the requests to RAINER can be logged (totally optional)
If you want to change your response to any of these questions later on, you can do so by using the following functions: rainer:::dataprot(), rainer:::github_token(), rainer:::language(), or rainer:::logging().
Getting your GitHub token
With a GitHub token you can access LLMs free of charge through GitHub Models. As RAINER uses these, you will need a personal GitHub token, which you can create by following these steps:
- Go to the GitHub page for managing your tokens: https://github.com/settings/tokens
- Make sure you selected ‘Tokens (classic)’ on the left
- Click on ‘Generate new token’ in the upper right corner
- Next, you need to choose the scopes for this token (what it’s allowed to do) and the expiration date (when the token stops working). For using RAINER and accessing LLMs you do not need to select any of the scopes.
- Success, you created your token! 🎉 Now make sure to copy it into RAINER and check that it works, before closing the website.
After the expiration date, the token (and RAINER) will stop working and you will need to create a new token. You can provide a new token to RAINER with rainer:::github_token().
Data protection
Access to the LLM is provided by GitHub. Hence, the usage of RAINER’s functions is an interaction between the user and GitHub (see GitHub’s data protection regulations). The following data of your R environment are included in the query:
- The currently opened document (e.g. script, R-markdown-document, …)
- The structure of all loaded datasets (only variable names, not the data itself)
- The name and type of all other loaded entities (e.g. variables, functions, …)
- The names of loaded packages
- The last error message
Further Development
RAINER was developed to help students with little or no prior programming experience in R. To improve the package, we would like to save a portion of queries for academic analysis.
The logged information contains 1. the same information as the prompt sent to GPT (see what the query contains above) and 2. the response of the LLM. This information is saved anonymously without the possibility of tracing back who sent the query.
Acceptance of logging is voluntary and the package does work without accepting it, too. The acceptance can be withdrawn at any time with the function rainer:::logging() and choosing no (as set per default).
The stored queries will only be used in an academic context and will only be published anonymized. The data will be deleted as soon as they are not used anymore in an academic context. In case of any questions, please contact us (rainer@stat.uni-muenchen.de). Thank you very much!